
It is shown that the observed errors in statistical modeling using pseudo-random numbers do not occur if the model examines linear systems with constant parameters, but in case models of nonlinear systems, higher order moments can have a Gaussian distribution.In this paper, we research the class $R(n,m)$ of substitutions on $n$-dimensional vector space produced by the binary left-shift registers of the length $n$ with one feedback $f(x_1,\dots,x_n)=x_1\oplus\psi(x_2,\dots,x_n)$ essentially depending on $m$ variables, $3\le m\le n$. It is supposed that the formation of the binary sequence output from the binary probabilistic element is produced using a physical noise process. These sequences are periodic and of length 2n and all 2n different binary n-tuples appear exactly one time in a periodic portion of the sequence. The shift register is called a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) if F is. One particular class of shift register sequences for which applications exist is the full length nonlinear shift register sequences.
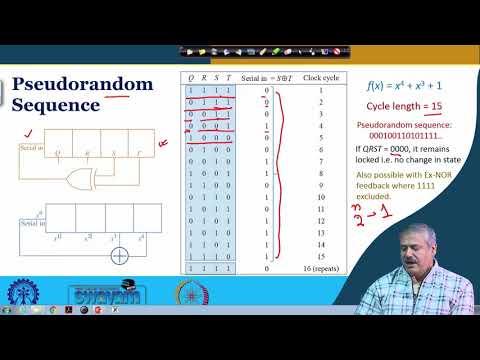
The received analytical dependencies can help in evaluating the statistical characteristics of the processes in solving problems of statistical modeling. A binary feedback shift register of order n is a mapping F from F 2 n into F 2 n of the form F: (x 0, x 1,, x n 1) (x 1, x 2,, x n 1, f (x 0, x 1,, x n 1)), where f is a Boolean function of n variables which is called the feedback function. Based on these studies, we obtained an analytic relation between the parameters of the binary sequence and parameters of a numerical sequence with the shift register output. In this article we introduce the concept of probabilistic binary element provides requirements, which ensure compliance with the criterion of "uniformity" in the implementation of the basic physical generators uniformly distributed random number sequences. The only linear function of single bits is xor, thus it is a. A linear feedback shift register (LFSR) is a shift register whose input bit is a linear function of its previous state. The maximal sequence consists of every possible state except the '0000' state. This block implements LFSR using a simple shift register generator (SSRG, or Fibonacci) configuration. The XOR gate provides feedback to the register that shifts bits from left to right.

While I am unable to find a paper which directly describes the methods, the paper A List of Maximum Period NLFSRs has just came up on eprint, which lists all NLFRSs with a period of 2 n 1, for n < 25.

The sequence generator generates a sequence of pseudorandom binary numbers using a linear-feedback shift register (LFSR). Given a binary shift register of n bits, a primitive binary nonlinear feedback shift register will generate a sequence with a period of 2 n 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
